State vs federal management of benefit programs explained
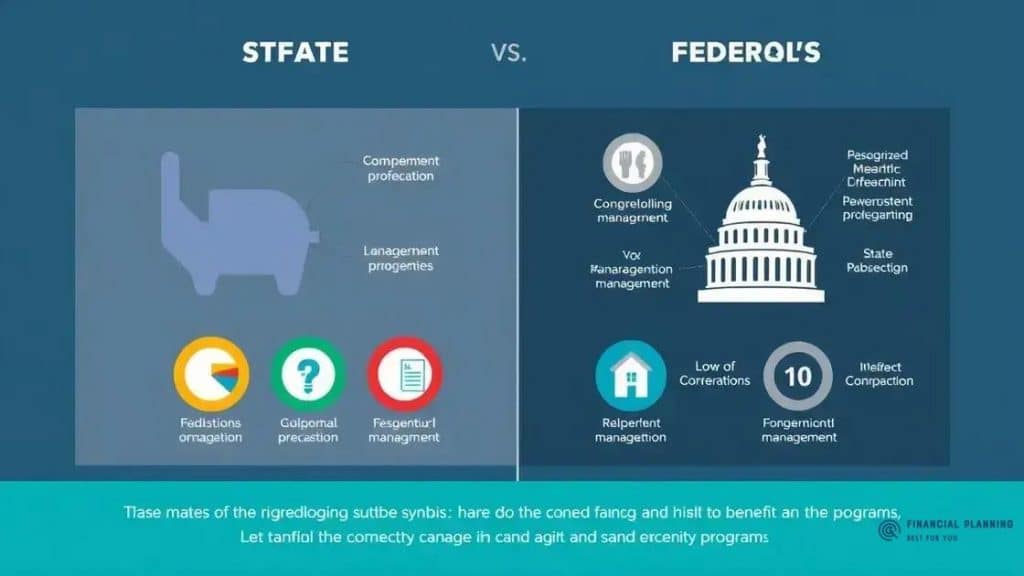
State vs federal management of benefit programs involves different approaches, where states tailor services to local needs while federal oversight ensures uniform standards and protections, impacting the accessibility and quality of benefits provided to citizens.
State vs federal management of benefit programs plays a crucial role in how benefits are distributed and accessed. Have you ever wondered how these two systems interact and affect real lives? Let’s dive into this complex relationship.
Understanding state management of benefit programs
Understanding how states manage benefit programs is essential for grasping the overall landscape of social services. Each state has its own policies, processes, and regulations that shape how benefits are delivered to residents. This can lead to significant differences in access and quality of assistance throughout the country.
Key Features of State Management
State management of benefit programs involves several key features that ensure that programs are tailored to local needs. These features enhance the effectiveness of social services and help address specific community issues:
- Customization: Each state can adapt programs to fit the unique demographics and needs of its population.
- Funding Allocation: States have the authority to allocate funds based on their specific budgetary priorities, affecting the quality and range of services.
- Program Integration: States often integrate benefit programs to streamline services, making it easier for individuals to access the assistance they need.
Moreover, state agencies work closely with local organizations to ensure that programs are effective and responsive. This collaboration helps build trust within communities and encourages utilization of available resources. For instance, many states leverage partnerships with non-profits to enhance outreach.
Challenges Faced by States
Despite the advantages, managing benefit programs at the state level is not without challenges. One significant issue is maintaining consistency between federal guidelines and state regulations. Sometimes, states may opt for enhanced services that exceed federal requirements, leading to confusion among applicants.
Another challenge is the availability of resources. States with limited budgets may struggle to provide comprehensive services, impacting the quality of benefits received. Furthermore, navigating the complex application processes can be daunting for residents, often resulting in underutilization of important programs.
In conclusion, understanding state management of benefit programs reveals a complex interplay of customization, challenges, and local needs. Each state’s approach affects not only the accessibility of benefits but also the overall welfare of its residents.
The role of federal oversight in benefit programs

The role of federal oversight in benefit programs is vital for maintaining standards and ensuring fairness across all states. This oversight helps to create a framework that states must follow, ensuring that programs are effective and equitable for all citizens.
Importance of Federal Guidelines
Federal guidelines set the foundation for how benefit programs operate. These guidelines ensure that all states follow specific requirements to meet the needs of beneficiaries. By having these standards in place, the federal government can:
- Ensure Quality: Establish minimum standards for benefit programs to maintain a consistent quality of service.
- Monitor Compliance: Regularly review state programs to ensure they comply with federal regulations.
- Protect Vulnerable Populations: Implement policies that specifically protect the most vulnerable groups, such as low-income families and disabled individuals.
In addition to these benefits, federal oversight allows for the allocation of resources to states that may struggle with funding. This support is essential for ensuring that all states can provide adequate services, regardless of their individual economic situations.
Collaboration Between Federal and State Governments
Collaboration between federal and state governments is key to enhancing the effectiveness of benefit programs. Federal agencies often work closely with state officials to implement new policies and share best practices. This cooperation can lead to innovations in program delivery, improving outcomes for beneficiaries.
Furthermore, the federal government provides technical assistance and funding opportunities that help states develop and improve their benefit programs. This collaborative environment encourages states to learn from each other, leading to more effective and efficient services.
While federal oversight is crucial, it’s also important to respect state autonomy. Every state has unique needs, and flexibility allows states to tailor programs to serve their communities best. This balance between oversight and autonomy helps create a responsive and adaptive benefit program system.
Comparative analysis of state and federal approaches
When exploring the comparative analysis of state and federal approaches to benefit programs, it becomes clear that both levels of government serve distinct but complementary roles. Each approach comes with its own set of advantages and challenges that impact how benefits are delivered to citizens.
Differences in Control
State and federal approaches differ significantly in terms of control and flexibility. State governments possess the authority to create and implement programs tailored to meet local needs. This flexibility allows them to:
- Address Unique Needs: States can modify programs based on specific demographic conditions, cultural factors, and economic situations.
- Experiment with Innovations: Some states act as testing grounds for new policies, which can lead to successful strategies that may later be adopted at the federal level.
- Enhance Local Engagement: Local governments often have a better understanding of community needs, enabling them to encourage greater participation among residents.
On the other hand, federal management establishes overarching standards, ensuring a minimum level of service that must be maintained nationwide. This federal oversight is essential for creating consistency and protecting rights across state lines, but it can also limit state flexibility.
Funding and Resources
The way funding is allocated also highlights differences between state and federal approaches. Federal programs typically provide baseline funding that states rely on, while states can supplement these funds based on their financial capacity. This can create disparities in service delivery, as wealthier states may provide more comprehensive benefits compared to those with limited resources.
Moreover, federal funding often comes with strict guidelines, which can lead to bureaucratic challenges for states trying to implement beneficial programs. While some states may excel in managing these requirements, others may struggle, leading to unequal access to necessary services.
In essence, the comparative analysis between state and federal approaches reveals a dynamic interplay that influences the efficiency and effectiveness of benefit programs. Each system presents its unique strengths, but achieving balance is crucial for serving the needs of all citizens efficiently.
Challenges in state vs federal management of benefits

Challenges in state vs federal management of benefits reveal complex dynamics that can affect the delivery of essential services. Navigating these challenges requires understanding the unique constraints faced by both levels of government.
Coordination Issues
One major challenge is the coordination between state and federal programs. With different goals and regulations, states may struggle to align their programs with federal guidelines. This often leads to confusion among beneficiaries. Important issues include:
- Duplicated Efforts: States may create programs that overlap with federal initiatives, wasting resources and creating unnecessary complexity.
- Inconsistent Services: Variability in services can occur when states interpret federal guidelines differently, leading to inequities in access to benefits.
- Communication Gaps: Ineffective communication between federal and state agencies can result in delays and misunderstandings in program implementation.
Effective collaboration is essential to address these coordination issues. Regular meetings and joint training sessions can help bridge gaps and improve understanding between state and federal agencies.
Resource Limitations
Resource limitations pose another significant challenge in managing benefits. States often face budget constraints, which can hinder their ability to implement effective programs. This situation may lead to:
- Limited Services: Some states may not offer the full range of benefits needed by their residents due to budget cuts or funding restrictions.
- Workforce Shortages: Recruiting and retaining qualified professionals in state agencies can be difficult, impacting service quality.
- Increased Pressure: As more individuals rely on social services during economic downturns, the demand for resources can outpace available services.
Addressing resource limitations requires federal support, such as increased funding or grants to help states meet growing demands. This can lead to more robust programs and improved outcomes for beneficiaries.
Ultimately, understanding the challenges in state vs federal management of benefits allows for more effective strategies aimed at overcoming obstacles. By working together, both levels of government can enhance service delivery and better support vulnerable populations.
Future trends in benefit program management
Future trends in benefit program management point towards a shift in how states and federal agencies will approach social service delivery. As technology evolves and demographics change, there is a growing emphasis on adopting more innovative methods to meet the needs of the population.
Technology Integration
One key trend is the integration of technology in benefit program management. This shift allows for improved accessibility and efficiency. By utilizing technology, agencies can:
- Streamline Processes: Automated systems can reduce paperwork and speed up processing times for applications.
- Enhance Communication: Technology facilitates better communication between agencies and beneficiaries, ensuring that individuals receive timely updates.
- Utilize Data Analytics: Agencies can analyze data to better understand community needs and adjust programs accordingly.
Employing these technologies not only increases operational efficiency but also improves the overall experience for applicants.
Focus on Inclusivity
Another trend is the increased focus on inclusivity in program design. Recognizing the diverse needs of the population, agencies are aiming to create programs that are accessible to all individuals. This entails:
- Personalized Services: Customizing services based on individual needs, backgrounds, and circumstances.
- Outreach Efforts: Implementing proactive outreach campaigns to educate underserved populations about their available benefits.
- Collaboration: Partnering with community organizations to ensure that assistance reaches those who need it most.
Inclusivity helps to bridge the gap for marginalized groups and ensures equitable access to resources.
Moreover, as the workforce evolves, states are exploring new training initiatives aimed at equipping staff with the skills needed for modern program management. Emphasizing professional development will enhance service delivery while responding to rapidly changing demands.
In summary, future trends in benefit program management suggest a more technology-driven, inclusive approach. As agencies adapt to new challenges, their focus will increasingly involve innovative solutions to ensure that all citizens can access the support they need.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions About State vs Federal Management of Benefit Programs
What are the main differences between state and federal management of benefit programs?
State management allows for tailored programs based on local needs, while federal oversight ensures uniform standards and protections across all states.
How is technology transforming benefit program management?
Technology is streamlining processes, improving communication, and enabling data analytics to better meet community needs.
What challenges do states face in managing benefit programs?
States often deal with coordination issues, resource limitations, and the pressure to comply with federal guidelines, which can impact service delivery.
What trends can we expect in the future of benefit program management?
Future trends include a greater focus on inclusivity, enhanced use of technology, and stronger collaboration between state and federal agencies.